udev: Function Flow for KOBJECT_UEVENT kernel group message
Table of Contents
Identifying the device #
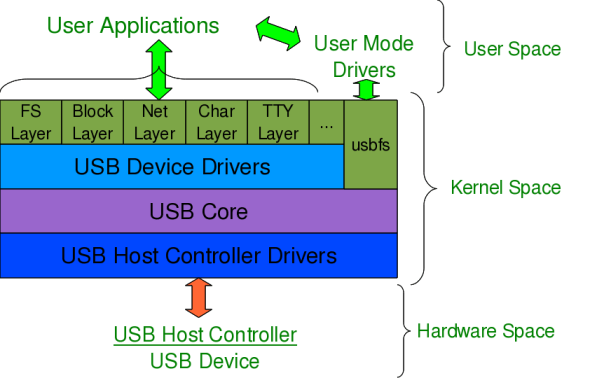
When a USB device is inserted to system, the very first initialization function to be started is drivers/usb/core/usb.c:usb_init(), written in [here].
The USB root hub driver (i.e. hcd) initiates the USB device initialization, the USB core takes the control and initializes an actual device structure struct usb_device.
linux/include/linux/usb.h
struct usb_device {
int devnum;
char devpath[16];
...
struct usb_device *parent;
struct usb_bus *bus;
struct usb_host_endpoint ep0;
struct device dev;
...
};
Then the USB core registers the usb device with device_register(&usb_device->dev) function.
int device_register(struct device *dev)
{
device_initialize(dev);
return device_add(dev);
}
The bus-specific fields of the usb_device structure are initialized by the USB core (e.g. devnum respresents an address on a USB bus) in device_initialize() call.
During handling device_add(), the kernel adds the kobject of the usb_device structure (at this time of the registration the usb device is shown in the sysfs directory [sysfs], which will be used by udevd), and the kernel emits KOBJECT_UEVENT messages with kernel message group.
linux/drivers/base/core.c: device_add()
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{
dev = get_device(dev);
...
/* first, register with generic layer. */
/* we require the name to be set before, and pass NULL */
error = kobject_add(&dev->kobj, dev->kobj.parent, NULL);
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent);
if (error)
goto attrError;
...
error = device_add_class_symlinks(dev);
if (error)
goto SymlinkError;
error = device_add_attrs(dev);
if (error)
goto AttrsError;
error = bus_add_device(dev);
if (error)
goto BusError;
error = dpm_sysfs_add(dev);
if (error)
goto DPMError;
device_pm_add(dev);
...
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
...
}
kobject_uevent() function is:
linux/lib/kobject_uevent.c
/**
* kobject_uevent - notify userspace by sending an uevent
*
* @kobj: struct kobject that the action is happening to
* @action: action that is happening
*
* Returns 0 if kobject_uevent() is completed with success or the
* corresponding error when it fails.
*/
int kobject_uevent(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action)
{
return kobject_uevent_env(kobj, action, NULL);
}
/**
* kobject_uevent_env - send an uevent with environmental data
*
* @kobj: struct kobject that the action is happening to
* @action: action that is happening
* @envp_ext: pointer to environmental data
*
* Returns 0 if kobject_uevent_env() is completed with success or the
* corresponding error when it fails.
*/
int kobject_uevent_env(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action, char *envp_ext[])
{
...
/* default keys */
retval = add_uevent_var(env, "ACTION=%s", action_string);
if (retval)
goto exit;
retval = add_uevent_var(env, "DEVPATH=%s", devpath);
if (retval)
goto exit;
retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SUBSYSTEM=%s", subsystem);
if (retval)
goto exit;
...
/* keys passed in from the caller */
if (envp_ext) {
for (i = 0; envp_ext[i]; i++) {
retval = add_uevent_var(env, "%s", envp_ext[i]);
if (retval)
goto exit;
}
}
retval = kobject_uevent_net_broadcast(kobj, env, action_string, devpath);
}
static int kobject_uevent_net_broadcast(struct kobject *kobj,
struct kobj_uevent_env *env,
const char *action_string,
const char *devpath)
{
...
/* kobjects currently only carry network namespace tags and they
* are the only tag relevant here since we want to decide which
* network namespaces to broadcast the uevent into.
*/
if (ops && ops->netlink_ns && kobj->ktype->namespace)
if (ops->type == KOBJ_NS_TYPE_NET)
net = kobj->ktype->namespace(kobj);
if (!net)
ret = uevent_net_broadcast_untagged(env, action_string,
devpath);
else
ret = uevent_net_broadcast_tagged(net->uevent_sock->sk, env,
action_string, devpath);
...
}
The final destination should be netlink_broadcast(), which is callbed by uevent_net_broadcast_(un)tagged() function.
static int uevent_net_broadcast_untagged(struct kobj_uevent_env *env,
const char *action_string,
const char *devpath)
{
...
/* send netlink message */
list_for_each_entry(ue_sk, &uevent_sock_list, list) {
struct sock *uevent_sock = ue_sk->sk;
...
retval = netlink_broadcast(uevent_sock, skb_get(skb), 0, 1,
GFP_KERNEL);
...
}
...
}
According to the signature of netlink_broadcast() function, 0 is portid and 1 is group number: equivalent to the value of GROUP_KERNEL in libudev library.
linux/net/netlink/af_netlink.c
int netlink_broadcast(struct sock *ssk, struct sk_buff *skb, u32 portid, u32 group, gfp_t allocation)
systemd/src/libsystemd/sd-device/device-monitor-private.h
typedef enum MonitorNetlinkGroup {
MONITOR_GROUP_NONE,
MONITOR_GROUP_KERNEL,
MONITOR_GROUP_UDEV,
_MONITOR_NETLINK_GROUP_MAX,
_MONITOR_NETLINK_GROUP_INVALID = -1,
} MonitorNetlinkGroup;
In summary, the kernel function call trace for sending GROUP_KERNEL udev message to udevd is as follows:
device_register()
device_add()
kobject_uevent()
kobject_uevent_env()
kobject_uevent_net_broadcast()
uevent_net_broadcast_untagged()
netlink_broadcast()