GPU Architecture Overview
Table of Contents
GPU Model #
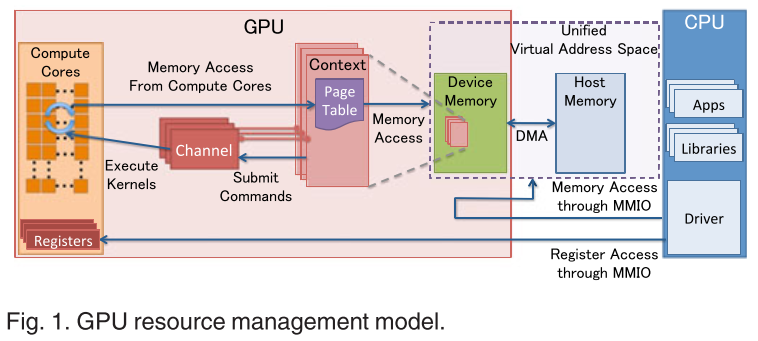
It explains several important designs that recent GPUs have adopted.
-
MMIO.
- The CPU communicates with the GPU via MMIO.
- Hardware engines for DMA are supported for transferring large amounts of data, however, commands should be written via MMIO.
- The I/O ports can be used to indirectly access the MMIO regions, but rarely used. An open source device driver Nouveau currently never uses it.
-
GPU Context.
- The context represents the state of the GPU computing.
- Owns a virtual address space in the GPU.
- Multiple active contexts can coexist on the GPU.
-
GPU Channel.
- Any operation (e.g. launching a kernel) is driven by commands issued from the CPU.
- The command stream is submitted to a hardware unit called a GPU channel.
- Each GPU context can have one or more GPU channels. Each GPU context contains GPU channel descriptors (each descriptor is created as a memory object in the GPU memory).
- Each GPU channel descriptor stores the settings of the channel, which includes a page table.
- Each GPU channel has a dedicated command buffer that is allocated in the GPU memory that is visible to the CPU through MMIO.
-
GPU Page Table.
- The GPU context is assigned using the GPU page table, which isolates the virtual address space from the others.
- The GPU page table is separated from the CPU page table.
- Resides in the GPU memory and its physical address is in a GPU channel descriptor.
- All the commands and programs submitted through the channel are executed in the corresponding GPU virtual address space.
- The GPU page tables translate a GPU virtual address into not only a GPU device physical address but also a host physical address. This enables the GPU page table to unify the GPU memory and host main memory into the unified GPU virtual address space.
-
PCIe BAR.
- The base address registers(BARs) of the PCIe, which work as the windows of MMIO, are configured at the boot time of the GPU.
- GPU control registers and GPU memory apertures are mapped onto the BARs.
- This mapped MMIO windows are used by the device driver to configure the GPU and to access the GPU memory.
-
PFIFO Engine.
- PFIFO is a special engine that the GPU commands are submitted through.
- Maintain multiple independent command queues, known as channels.
- A command queue is a ring buffer with the put and get pointers.
- All accesses to channel control area are intercepted by PFIFO engine for execution.
- GPU driver uses a channel descriptor to store the settings for associated channel.
- Nouveau says that the PFIFO engine of the GPU reads commands from a section of memory, and relays them to the PGRAPH engine. (Maybe this for graphics?)
-
Bo
- Nouveau and gdev uses bo really a lot.
- Buffer Object (bo). A block of memory. It can store a texture, a render target, shader code, … everything.
References #
- Yusuke Suzuki et al. GPUvm: GPU Virtualization at the Hypervisor". IEEE Transactions on Computers. 2016
- Hong-Cyuan Hsu et al. G-KVM: A Full GPU Virtualization on KVM". IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology. 2016
- Nouveau Terms. [Online] (Accessed at Apr 27, 2017. Documentation version Aug 24, 2013)
- Nouveau Team. nVidia Hardware Documentation. [Online] (Accessed at Apr 27, 2017. Documentation version Apr 18, 2017)